
Tachikawa Ki94 I Destination's Journey
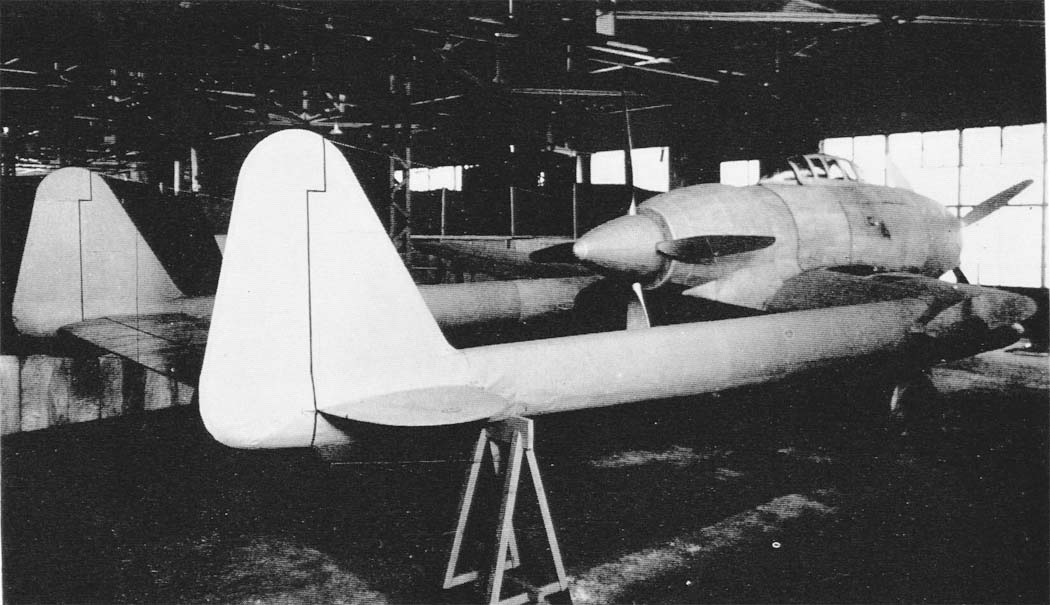
The term Tachikawa Ki-94 refers to two designs of the Tachikawa Hikoki K.K. aircraft factory. The first was a twin-boom monoplane with two 1,641 kW (2,201 hp) Mitsubishi Ha211 18-cylinder engines, driving two 4-blade propellers in a push-pull configuration. The very heavy armament that should have been mounted on the aircraft (two 37 mm/1.46 in.

Tachikawa Ki94 I Destination's Journey
Realising that things weren't going their way, the Imperial Japanese Army issued specifications in mid-1942 for new interceptors to tackle bombers that may a.
Tachikawa Ki94
The term Tachikawa Ki-94 refers to two designs of the Tachikawa Hikoki K.K. aircraft factory. The first was a twin-boom monoplane with two 1,641 kW (2,200 hp) Mitsubishi Ha-211 18 cylinder engines, driving two 4-blade propellors in a push-pull configuration. The very heavy armament that should have been mounted on the aircraft (two 37 mm/1.46 in and two 30 mm/1.18 in cannons, should have been.

Tachikawa Ki94I Emmas Planes
Media in category "Tachikawa Ki-94" The following 11 files are in this category, out of 11 total.

World of Warplanes Tachikawa Ki94II gameplay YouTube
The Tachikawa Ki-94-I and -II - although oddly these were completely different aircraft. Allow me to explain. With the catastrophic defeat at the Battle of Midway in June 1942, which saw the loss of four of Japan's fleet carriers, let only much of the cream of their naval air arm, the Japanese Army realized that Imperial Japan might soon be.

Japanese IIWW fighter Tachikawa Ki94II HighAltitude Interceptor RS Models 92020
Tachikawa Ki-94-I Heavy Fighter VII tier 1. Project for a high-speed fighter with heavy armament. A wooden mock-up was built by October 1943. However, the concept of the Ki-94-I was judged by the Japanese Army Air Force as too unconventional. The Tachikawa company was tasked to build an aircraft with a more conventional design.

Tachikawa Ki94I/II
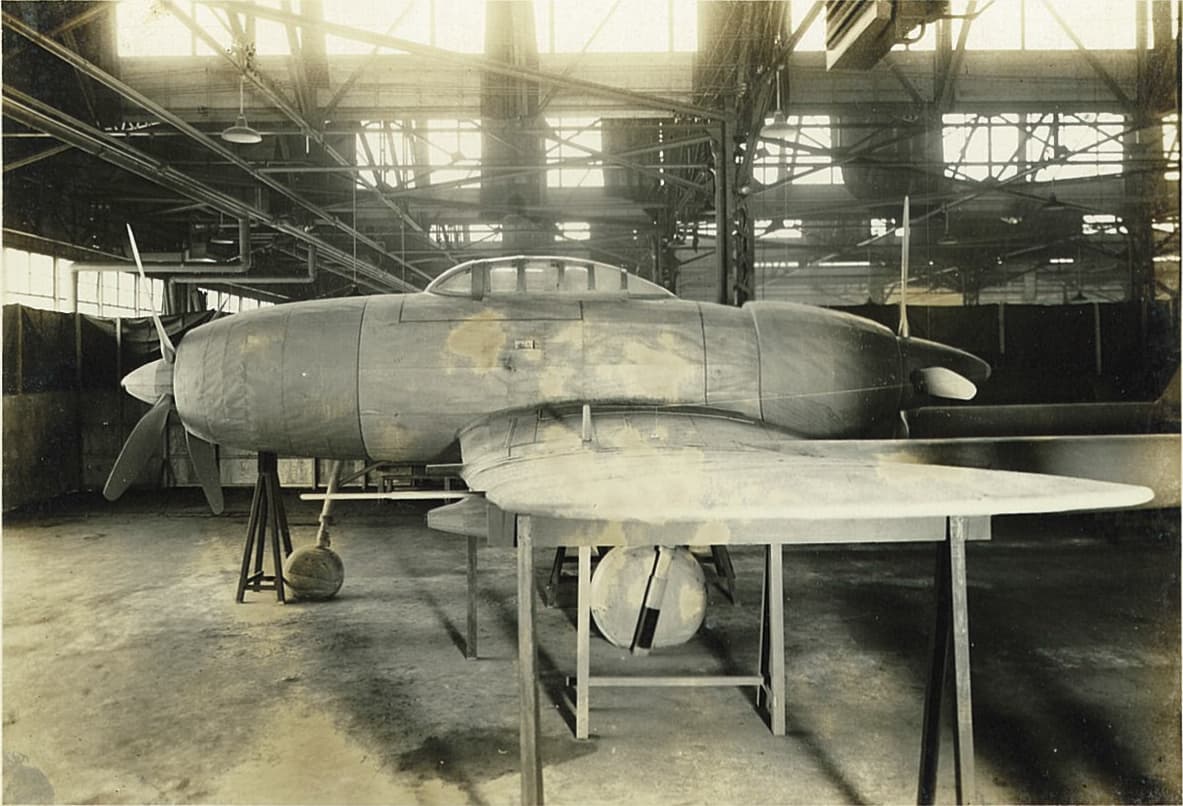
The Tachikawa Ki-94 was designed to meet a request by the Japanese Army for a heavily-armed high-altitude fighter fitted with a pressure cabin and capable of reaching a top speed of 800 km/h (497 mph), with a maximum range of 3000 km (1,864 miles). The unconventional design that resulted was a large twin-boom monoplane powered by two 2,200 hp.

Tachikawa Ki94 Photos, History, Specification
First flight of model of Japanese Fighter Aircraft Tachikawa KI 94 I, キ94 (航空機)Original: A twin-boom monoplane, push-pull configuration, wingspan 15 m,constr.

Tachikawa Ki94II Wwii aircraft, Military aircraft, Aviation art
The Tachikawa Ki-94 was a single-seat fighter-Interceptor aircraft project undertaken by the Tachikawa Aircraft Company and to be operated by the Imperial Japanese Army. The project refers to two aircraft designs: the Ki-94-I and the Ki-94-II, both of which did not advance beyond the mock-up and prototype stage respectively.

Tachikawa Ki94II Fighters 戦闘機, 軍用機, 空軍
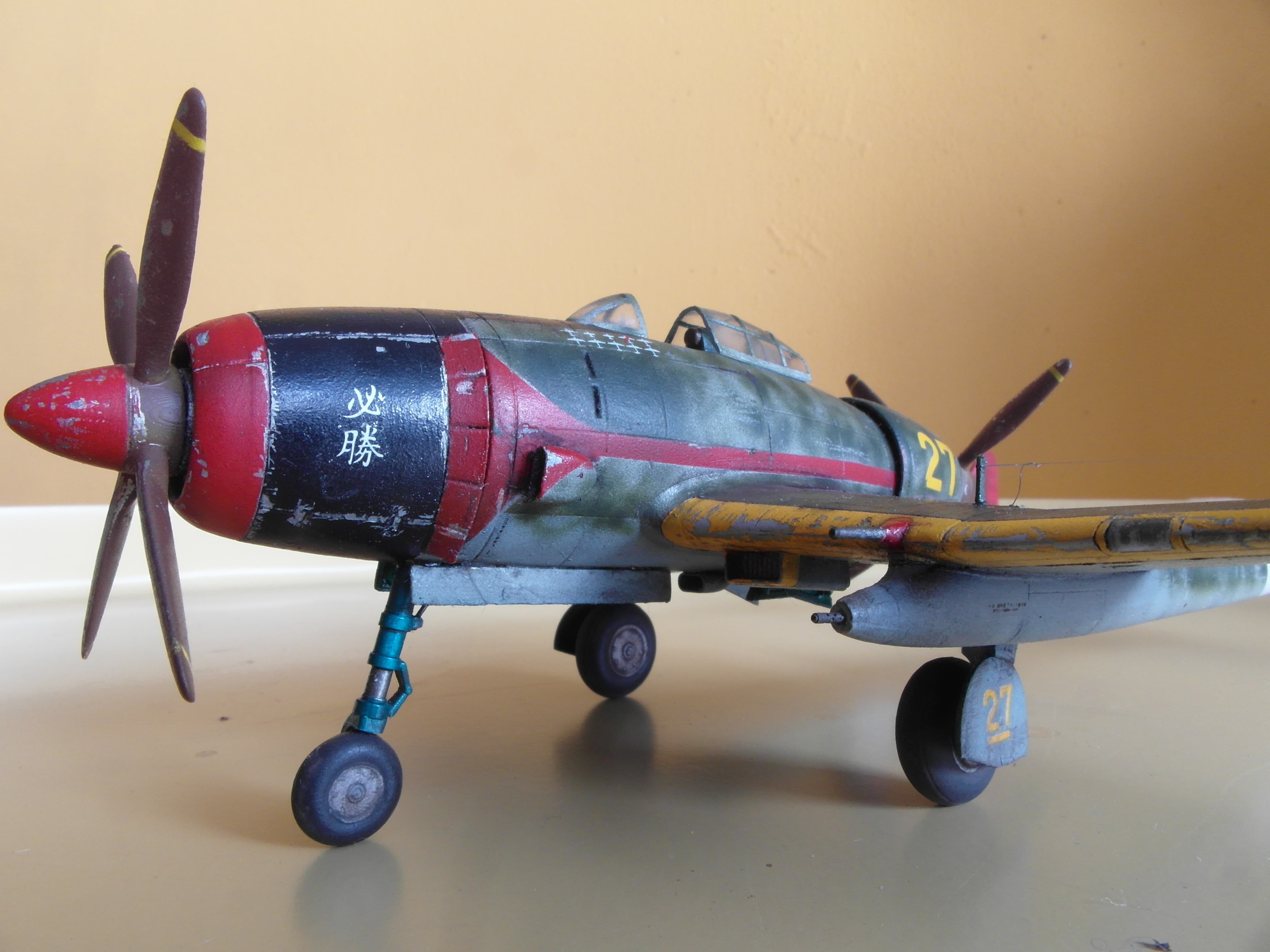
Tachikawa undertook two late-war programs intended as bomber interceptors for the Army under the "Ki-94" designation. As the American Boeing B-29 "Superfortress" high-altitude heavy bomber became the primary concern for the Japanese homeland, a high-altitude fighter capable of intercepting these machines was in order.

Tachikawa Ki94I Emmas Planes
The development of the Ki-94 started in 1942 when the need for a high altitude interceptor arose. The Koku Hombu approached both Tachikawa and Nakajima to develop a pressurized aircraft which could fly with 800 km/h and had a 3000 km range. After review in February 1943, the Koku Hombu deemed the aircraft too unorthodox and too difficult to.

TACHIKAWA KI 94 I, 3rd and 4th flight YouTube
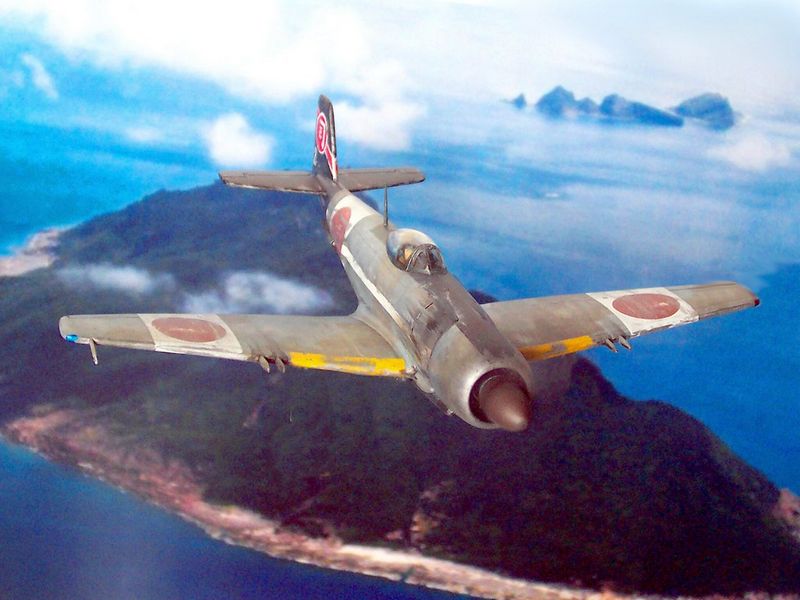
The Tachikawa KI-94 II was designed late in the Second World War as a high-altitude interceptor specifically to combat B-29s. With a supposedly laminar flow wing, six bladed prop driven by a 2400 hp 18 cylinder turbocharged engine giving an estimated top speed of around 422 MPH and a ceiling of 14,680 m, this would have been some performer.

Рисунок Tachikawa Ki94II на рабочий стол Авиация War Wallpapers
Tachikawa Ki-94 History. Many of the aircraft developed by Japan when it surrendered in 1945 were retired in their state (if they had not been destroyed by ruthless air strikes by the Japanese themselves or by the Allies). Tachikawa conducted two postwar programs under the name "Ki-94" to provide the Army with interceptor bombers.

Tachikawa Ki94II (A + V Model, Resin) ModelPlanes.de
Working on the Ki-94-II aircraft, Tachikawa proceeded from a new application, which assumed the satisfaction of the same flight performance requirements as the competing aircraft Nakajima Ki-87. The new Ki-94-II high-altitude fighter project was developed under the leadership of Chief Designer Tatsuo Hasegawa. The new aircraft was a single-seat.

Japanese IIWW fighter Tachikawa Ki94II Prototype RS Models 92019
Tachikawa Ki-94 II. The Tachikawa Ki-94 II was a single-seat, piston-engine monoplane fighter, developed for the Imperial Japanese Army Air Force along the same requirements as the Nakajima Ki-87, which had been the Army's fall-back design for the original Tachikawa Ki-94 I Intended to counter B-29 raids, it was optimized for high-altitude interception with a pressurized cockpit and heavy.

Tachikawa Ki94I/II
The aircraft proposed by Tachikawa, which received the designation Ki-94 (later Ki-94-I), was of highly unconventional design. The aircraft was a large twin-boom monoplane powered by two 2,200 hp Mitsubishi Ha-211 Ru eighteen-cylinder air-cooled radials which were mounted fore and aft of the pilot's cockpit and drove four-blade tractor and.